#oracle to postgresql
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Elevate Your Database Strategy: How Newt Global Simplifies the Oracle to PostgreSQL Shift
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, organizations are increasingly searching for database solutions that provide not only robust performance but also cost efficiency and flexibility. Oracle has long been a leading choice for enterprises due to its powerful features and reliability. However, in recent years, PostgreSQL has emerged as a formidable alternative, particularly for those seeking a more open, scalable, and cost-effective database management system. This blog explores why organizations are migrating from Oracle to PostgreSQL and how this transition can be a game-changer for your business.
Why Migrate from Oracle to PostgreSQL?
1. Cost Efficiency
One of the most compelling reasons to migrate from Oracle to PostgreSQL is cost savings. Oracle’s licensing fees can be prohibitively expensive, particularly for small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) or startups. PostgreSQL, being open-source, eliminates the need for costly licenses and maintenance fees. Organizations can significantly reduce their Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) by moving to PostgreSQL and reallocating funds to other critical areas of the business.
2. Open Source Advantage
PostgreSQL’s open-source nature means that it benefits from a vast, global community of developers continuously working on updates, bug fixes, and feature enhancements. This community-driven development ensures that PostgreSQL remains at the forefront of technological advancements. In contrast, Oracle’s closed-source nature limits user flexibility and innovation, as changes are controlled solely by Oracle Corporation.
3. Flexibility and Customization
PostgreSQL is renowned for its flexibility, offering extensive customization options that allow organizations to tailor the database to their specific needs. It supports advanced data types, such as JSONB for JSON data storage, and custom extensions, enabling businesses to build complex applications with ease. 4. Scalability
PostgreSQL’s scalability is another key factor driving migrations. Whether your organization is handling a few gigabytes or several terabytes of data, PostgreSQL can scale horizontally and vertically to meet your needs. It also supports multi-master replication and sharding, which are essential for distributed systems and high-availability environments. Oracle provides similar features, but often at a significant cost, making PostgreSQL an attractive alternative for growing businesses.
5. Performance
While Oracle has traditionally been associated with high performance, PostgreSQL has made significant strides in this area, particularly with its ability to handle complex queries and large volumes of data. PostgreSQL’s advanced indexing techniques, such as GiST, GIN, and BRIN indexes, enhance query performance, making it a viable option for performance-critical applications. 6. Support for a wide extent of information Sorts
PostgreSQL moreover gives a wide extent of ordering choices, making it adaptable and versatile to diverse use cases. It supports both organized and unstructured information, allowing organizations to store and analyze diverse sorts of data. It also allows for the definition of custom information sorts, administrators, and functions, empowering solutions to be tailored to specific necessities.
7. Compliance and Security with ACID
PostgreSQL adheres to stringent compliance standards, including ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) properties, which ensure data integrity and reliability. While Oracle is also highly secure, PostgreSQL provides these features at no additional cost, making it an excellent choice for organizations with stringent security requirements. Accelerate Your Database Transformation- Oracle to PostgreSQL Migration Made Easy Migrating from Oracle to PostgreSQL is increasingly seen as a strategic move for organizations aiming to modernize their IT infrastructure. These tools automate much of the data transfer, schema conversion, and code rewriting needed to shift from Oracle’s proprietary environment to PostgreSQL’s open-source platform. This automation not as it were decreases the hazard of human mistake but too quickens the migration timeline, allowing businesses to rapidly harvest the benefits of PostgreSQL. Additionally, PostgreSQL’s robust support for modern data types, indexing methods, and scalability features ensures that migrated applications perform efficiently, even under high load. The migration process also presents an opportunity to revisit and optimize database structures, leading to improved performance and lower operational costs. In essence, PostgreSQL migration is not just a database switch, but a pathway to greater innovation and agility. Newt Global Leads the Way- Enhancing IT Infrastructure Through Oracle to PostgreSQL Migration PostgreSQL offers a dynamic and flexible environment that empowers businesses to innovate while freeing them from the limitations and high costs associated with Oracle's proprietary systems. This migration, however, requires careful planning and execution to ensure a smooth transition without disrupting business operations.
Newt Global, a recognized leader in cloud migration and digital transformation services, excels in guiding organizations through the complexities of database migration. With its deep industry expertise and comprehensive suite of services, Newt Global not only accelerates the migration process but also ensures that businesses fully leverage the advanced capabilities of PostgreSQL. Partnering with Newt Global means more than just migrating databases; it's about transforming your IT infrastructure to meet future demands. Thanks For Reading
For More Information, Visit Our Website: https://newtglobal.com/
0 notes
Text






Simple Logic transformed a global enterprise’s database performance with seamless cloud migration!
Challenges: Frequent FDW failures disrupting operations 🔌 Downtime from limited resources ⏳ Delays causing customer dissatisfaction 😟 Manual workarounds slowing tasks 🐢
Our Solution: Migrated DB to AWS for scalable performance ☁️ Fixed FDW stability issues 🔧 Optimized PostgreSQL & Oracle integration 🚀 Resolved resource bottlenecks 🛠️
The Results: Stable cloud setup with zero downtime ✅ Faster processing, happier users ⚡😊
Ready to boost your database performance? 📩 [email protected] 📞 +91 86556 16540
💻 Explore insights on the latest in #technology on our Blog Page 👉 https://simplelogic-it.com/blogs/
🌐For more details, please visit our official website����https://simplelogic-it.com/
👉 Contact us here: https://simplelogic-it.com/contact-us/
#CloudMigration#PostgreSQL#ITSolutions#Database#Data#LimitedResources#AWS#Oracle#StabilityIssues#Cloud#CloudServices#Downtime#DatabasePerformance#ScalablePerformance#SimpleLogicIT#MakingITSimple#MakeITSimple#SimpleLogic#ITServices#ITConsulting
0 notes
Text
Introducing Datastream GCP’s new Stream Recovery Features

Replication pipelines can break in the complicated and dynamic world of data replication. Restarting replication with little impact on data integrity requires a number of manual procedures that must be completed after determining the cause and timing of the failure.
With the help of Datastream GCP‘s new stream recovery capability, you can immediately resume data replication in scenarios like database failover or extended network outages with little to no data loss.
Think about a financial company that replicates transaction data to BigQuery for analytics using DataStream from their operational database. A planned failover to a replica occurs when there is a hardware failure with the primary database instance. Due to the unavailability of the original source, Datastream’s replication pipeline is malfunctioning. In order to prevent transaction data loss, stream recovery enables replication to continue from the failover database instance.
Consider an online shop that replicates user input to BigQuery for sentiment analysis using BigQuery ML utilising Datastream. An extended network disruption breaks the source database connection. Some of the updates are no longer accessible on the database server by the time network connectivity is restored. Here, the user can rapidly resume replication from the first available log point thanks to stream recovery. For ongoing sentiment analysis and trend identification, the merchant prioritises obtaining the most recent data, even though some feedback may be lost.
The advantages of recovering streams
Benefits of stream recovery include the following
Reduced data loss: Get back data lost by events like unintentional log file deletion and database instance failovers.
Minimise downtime: Get back up and running as soon as possible to resume continuous CDC consumption and swiftly restore your stream.
Recovery made easier: A user-friendly interface makes it simple to retrieve your stream.
Availables of Datastream GCP
Minimise latency in data replication and synchronisation
Reduce the impact on source performance while ensuring reliable, low-latency data synchronization across diverse databases, storage systems, and applications.
Adapt to changing needs using a serverless design
Quickly get up and running with a simple, serverless application that scales up and down without any hassle and requires no infrastructure management.
Google Cloud services offer unparalleled flexibility
Utilise the best Google Cloud services, such as BigQuery, as Spanner, Dataflow, and Data Fusion, to connect and integrate data throughout your company.
Important characteristics
The unique strategy of Datastream GCP
Data streaming via relational databases
Your MySQL, PostgreSQL, AlloyDB, SQL Server, and Oracle databases can be read and updated by Datastream, which then transfers the changes to BigQuery, Cloud SQL, Cloud Storage, and Spanner. It consistently broadcasts every event as it happens and is Google native and agentless. More than 500 trillion events are processed monthly by Datastream.
Robust pipelines with sophisticated recovery
Unexpected disruptions may incur high expenses. You can preserve vital business activities and make defensible decisions based on continuous data pipelines thanks to Datastream GCP‘s strong stream recovery, which reduces downtime and data loss.
Resolution of schema drift
Datastream GCP enables quick and easy resolution of schema drift when source schemas change. Every time a schema is changed, Datastream rotates the files, adding a new file to the target bucket. With a current, versioned Schema Registry, original source data types are only a call away via an API.
Safe by design
To safeguard data while it’s in transit, Datastream GCP offers a variety of private, secure connectivity options. You can relax knowing your data is safe while it streams because it is also encrypted while it is in transit and at rest.
The application of stream recovery
Depending on the particular failure circumstance and the availability of current log files, stream recovery offers you a few options to select from. You have three options when it comes to MySQL and Oracle: stream from the most recent position, skip the current position and stream from the next available position, or retry from the current log position. Additionally, you can provide the stream a precise log position to resume from for example, the Log Sequence Number (LSN) or Change Sequence Number (CSN) giving you more precise control over making sure that no data is lost or duplicated in the destination.
You can tell Datastream to start streaming again from the new replication slot after creating a new one in your PostgreSQL database for PostgreSQL sources.
From a given position, begin a stream
Apart from stream recovery, there are several situations in which you might need to begin or continue a stream from a particular log location. For instance, when the source database is being upgraded or moved, or when historical data from a particular point in time (where the historical data terminates) is already present in the destination and you would like to merge it. In these situations, you can utilise the stream recovery API to set a starting position before initiating the stream.
Get going
For all available Datastream sources across all Google Cloud regions, stream recovery is now widely accessible via the Google Cloud dashboard and API.
Read more on Govindhtech.com
#DatastreamGCP#BigQuery#GoogleCloud#spanner#dataflow#BigQueryML#SQLServer#PostgreSQL#oracle#MySQL#cloudstorage#news#technews#technology#technologynews#technologytrends#govindhtech
1 note
·
View note
Text
Mastering Aggregate Functions in SQL: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction to SQL: In the realm of relational databases, Structured Query Language (SQL) serves as a powerful tool for managing and manipulating data. Among its many capabilities, SQL offers a set of aggregate functions that allow users to perform calculations on groups of rows to derive meaningful insights from large datasets.

Learn how to use SQL aggregate functions like SUM, AVG, COUNT, MIN, and MAX to analyze data efficiently. This comprehensive guide covers syntax, examples, and best practices to help you master SQL queries for data analysis.
#aggregate functions#sql aggregate functions#aggregate functions in sql#aggregate functions in dbms#aggregate functions in sql server#aggregate functions in oracle#aggregate function in mysql#window function in sql#aggregate functions sql#best sql aggregate functions#aggregate functions and grouping#aggregate functions dbms#aggregate functions mysql#aggregate function#sql window functions#aggregate function tutorial#postgresql aggregate functions tutorial.
0 notes
Text
What are partitions: partitions are database object, it is basically splitting large table into small multiple parts.
It is very helpful for getting quick query results.
It will help to improve database performance.
Types of partitions
Range partitions
Key partitions
Sub partitions ..etc.

#dataanalytics#life#beautiful#data#database#DBA#partitions#partitioning#oracle#postgresql#mysql database#mysql#sql#plsql#table#index
0 notes
Text
#learn#free#resource#python#r#postgresql#chatgpt#tableau#power bi#excel#scala#apache spark#shell#git#oracle#programming#software
0 notes
Text
Structured Query Language (SQL): A Comprehensive Guide
Structured Query Language, popularly called SQL (reported "ess-que-ell" or sometimes "sequel"), is the same old language used for managing and manipulating relational databases. Developed in the early 1970s by using IBM researchers Donald D. Chamberlin and Raymond F. Boyce, SQL has when you consider that end up the dominant language for database structures round the world.
Structured query language commands with examples
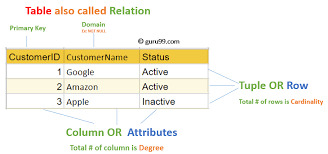
Today, certainly every important relational database control system (RDBMS)—such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, SQL Server, and SQLite—uses SQL as its core question language.
What is SQL?
SQL is a website-specific language used to:
Retrieve facts from a database.
Insert, replace, and delete statistics.
Create and modify database structures (tables, indexes, perspectives).
Manage get entry to permissions and security.
Perform data analytics and reporting.
In easy phrases, SQL permits customers to speak with databases to shop and retrieve structured information.
Key Characteristics of SQL
Declarative Language: SQL focuses on what to do, now not the way to do it. For instance, whilst you write SELECT * FROM users, you don’t need to inform SQL the way to fetch the facts—it figures that out.
Standardized: SQL has been standardized through agencies like ANSI and ISO, with maximum database structures enforcing the core language and including their very own extensions.
Relational Model-Based: SQL is designed to work with tables (also called members of the family) in which records is organized in rows and columns.
Core Components of SQL
SQL may be damaged down into numerous predominant categories of instructions, each with unique functions.
1. Data Definition Language (DDL)
DDL commands are used to outline or modify the shape of database gadgets like tables, schemas, indexes, and so forth.
Common DDL commands:
CREATE: To create a brand new table or database.
ALTER: To modify an present table (add or put off columns).
DROP: To delete a table or database.
TRUNCATE: To delete all rows from a table but preserve its shape.
Example:
sq.
Copy
Edit
CREATE TABLE personnel (
id INT PRIMARY KEY,
call VARCHAR(one hundred),
income DECIMAL(10,2)
);
2. Data Manipulation Language (DML)
DML commands are used for statistics operations which include inserting, updating, or deleting information.
Common DML commands:
SELECT: Retrieve data from one or more tables.
INSERT: Add new records.
UPDATE: Modify existing statistics.
DELETE: Remove information.
Example:
square
Copy
Edit
INSERT INTO employees (id, name, earnings)
VALUES (1, 'Alice Johnson', 75000.00);
three. Data Query Language (DQL)
Some specialists separate SELECT from DML and treat it as its very own category: DQL.
Example:
square
Copy
Edit
SELECT name, income FROM personnel WHERE profits > 60000;
This command retrieves names and salaries of employees earning more than 60,000.
4. Data Control Language (DCL)
DCL instructions cope with permissions and access manage.
Common DCL instructions:
GRANT: Give get right of entry to to users.
REVOKE: Remove access.
Example:
square
Copy
Edit
GRANT SELECT, INSERT ON personnel TO john_doe;
five. Transaction Control Language (TCL)
TCL commands manage transactions to ensure data integrity.
Common TCL instructions:
BEGIN: Start a transaction.
COMMIT: Save changes.
ROLLBACK: Undo changes.
SAVEPOINT: Set a savepoint inside a transaction.
Example:
square
Copy
Edit
BEGIN;
UPDATE personnel SET earnings = income * 1.10;
COMMIT;
SQL Clauses and Syntax Elements
WHERE: Filters rows.
ORDER BY: Sorts effects.
GROUP BY: Groups rows sharing a assets.
HAVING: Filters companies.
JOIN: Combines rows from or greater tables.
Example with JOIN:
square
Copy
Edit
SELECT personnel.Name, departments.Name
FROM personnel
JOIN departments ON personnel.Dept_id = departments.Identity;
Types of Joins in SQL
INNER JOIN: Returns statistics with matching values in each tables.
LEFT JOIN: Returns all statistics from the left table, and matched statistics from the right.
RIGHT JOIN: Opposite of LEFT JOIN.
FULL JOIN: Returns all records while there is a in shape in either desk.
SELF JOIN: Joins a table to itself.
Subqueries and Nested Queries
A subquery is a query inside any other query.
Example:
sq.
Copy
Edit
SELECT name FROM employees
WHERE earnings > (SELECT AVG(earnings) FROM personnel);
This reveals employees who earn above common earnings.
Functions in SQL
SQL includes built-in features for acting calculations and formatting:
Aggregate Functions: SUM(), AVG(), COUNT(), MAX(), MIN()
String Functions: UPPER(), LOWER(), CONCAT()
Date Functions: NOW(), CURDATE(), DATEADD()
Conversion Functions: CAST(), CONVERT()
Indexes in SQL
An index is used to hurry up searches.
Example:
sq.
Copy
Edit
CREATE INDEX idx_name ON employees(call);
Indexes help improve the performance of queries concerning massive information.
Views in SQL
A view is a digital desk created through a question.
Example:
square
Copy
Edit
CREATE VIEW high_earners AS
SELECT call, salary FROM employees WHERE earnings > 80000;
Views are beneficial for:
Security (disguise positive columns)
Simplifying complex queries
Reusability
Normalization in SQL
Normalization is the system of organizing facts to reduce redundancy. It entails breaking a database into multiple related tables and defining overseas keys to link them.
1NF: No repeating groups.
2NF: No partial dependency.
3NF: No transitive dependency.
SQL in Real-World Applications
Web Development: Most web apps use SQL to manipulate customers, periods, orders, and content.
Data Analysis: SQL is extensively used in information analytics systems like Power BI, Tableau, and even Excel (thru Power Query).
Finance and Banking: SQL handles transaction logs, audit trails, and reporting systems.
Healthcare: Managing patient statistics, remedy records, and billing.
Retail: Inventory systems, sales analysis, and consumer statistics.
Government and Research: For storing and querying massive datasets.
Popular SQL Database Systems
MySQL: Open-supply and extensively used in internet apps.
PostgreSQL: Advanced capabilities and standards compliance.
Oracle DB: Commercial, especially scalable, agency-degree.
SQL Server: Microsoft’s relational database.
SQLite: Lightweight, file-based database used in cellular and desktop apps.
Limitations of SQL
SQL can be verbose and complicated for positive operations.
Not perfect for unstructured information (NoSQL databases like MongoDB are better acceptable).
Vendor-unique extensions can reduce portability.
Java Programming Language Tutorial
Dot Net Programming Language
C ++ Online Compliers
C Language Compliers
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
5 useful tools for engineers! Introducing recommendations to improve work efficiency
Engineers have to do a huge amount of coding. It’s really tough having to handle other duties and schedule management at the same time. Having the right tools is key to being a successful engineer.
Here are some tools that will help you improve your work efficiency.
1.SourceTree
“SourceTree” is free Git client software provided by Atlassian. It is a tool for source code management and version control for developers and teams using the version control system called Git. When developers and teams use Git to manage projects, it supports efficient development work by providing a visualized interface and rich functionality.
2.Charles
“Charles” is an HTTP proxy tool for web development and debugging, and a debugging proxy tool for capturing HTTP and HTTPS traffic, visualizing and analyzing communication between networks. This allows web developers and system administrators to observe requests and responses for debugging, testing, performance optimization, and more.
3.iTerm2
“iTerm2” is a highly functional terminal emulator for macOS, and is an application that allows terminal operations to be performed more comfortably and efficiently. It offers more features than the standard Terminal application. It has rich features such as tab splitting, window splitting, session management, customizable appearance, and script execution.
4.Navicat
Navicat is an integrated tool for performing database management and development tasks and supports many major database systems (MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQLite, Oracle, SQL Server, etc.). Using Navicat, you can efficiently perform tasks such as database structure design, data editing and management, SQL query execution, data modeling, backup and restore.
5.CodeLF
CodeLF (Code Language Framework) is a tool designed to help find, navigate, and understand code within large source code bases. Key features include finding and querying symbols such as functions, variables, and classes in your codebase, viewing code snippets, and visualizing relationships between code. It can aid in efficient code navigation and understanding, increasing productivity in the development process.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
With SQL Server, Oracle MySQL, MongoDB, and PostgreSQL and more, we are your dedicated partner in managing, optimizing, securing, and supporting your data infrastructure.
For more, visit: https://briskwinit.com/database-services/
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
The Ultimate Guide to Migrating from Oracle to PostgreSQL: Challenges and Solutions
Challenges in Migrating from Oracle to PostgreSQL
Migrating from Oracle to PostgreSQL is a significant endeavor that can yield substantial benefits in terms of cost savings, flexibility, and advanced features. Understanding these challenges is crucial for ensuring a smooth and successful transition. Here are some of the essential impediments organizations may face during the migration:
1. Schema Differences
Challenge: Oracle and PostgreSQL have different schema structures, which can complicate the migration process. Oracle's extensive use of features such as PL/SQL, packages, and sequences needs careful mapping to PostgreSQL equivalents.
Solution:
Schema Conversion Tools: Utilize tools like Ora2Pg, AWS Schema Conversion Tool (SCT), and EDB Postgres Migration Toolkit to automate and simplify the conversion of schemas.
Manual Adjustments: In some cases, manual adjustments may be necessary to address specific incompatibilities or custom Oracle features not directly supported by PostgreSQL.
2. Data Type Incompatibilities
Challenge: Oracle and PostgreSQL support diverse information sorts, and coordinate mapping between these sorts can be challenging. For illustration, Oracle's NUMBER information sort has no coordinate identical in PostgreSQL.
Solution:
Data Type Mapping: Use migration tools that can automatically map Oracle data types to PostgreSQL data types, such as PgLoader and Ora2Pg.
Custom Scripts: Write custom scripts to handle complex data type conversions that are not supported by automated tools.
3. Stored Procedures and Triggers
Challenge: Oracle's PL/SQL and PostgreSQL's PL/pgSQL are similar but have distinct differences that can complicate the migration of stored procedures, functions, and triggers.
Solution:
Code Conversion Tools: Use tools like Ora2Pg to convert PL/SQL code to PL/pgSQL. However, be prepared to review and test the converted code thoroughly.
Manual Rewriting: For complex procedures and triggers, manual rewriting and optimization may be necessary to ensure they work correctly in PostgreSQL.
4. Performance Optimization
Challenge: Performance tuning is essential to ensure that the PostgreSQL database performs as well or better than the original Oracle database. Differences in indexing, query optimization, and execution plans can affect performance.
Solution:
Indexing Strategies: Analyze and implement appropriate indexing strategies tailored to PostgreSQL.
Query Optimization: Optimize queries and consider using PostgreSQL-specific features, such as table partitioning and advanced indexing techniques.
Configuration Tuning: Adjust PostgreSQL configuration parameters to suit the workload and hardware environment.
5. Data Migration and Integrity
Challenge: Ensuring data judgment during the migration process is critical. Huge volumes of information and complex information connections can make data migration challenging.
Solution:
Data Migration Tools: Use tools like PgLoader and the data migration features of Ora2Pg to facilitate efficient and accurate data transfer.
Validation: Perform thorough data validation and integrity checks post-migration to guarantee that all information has been precisely exchanged and is steady.
6. Application Compatibility
Challenge: Applications built to interact with Oracle may require modifications to work seamlessly with PostgreSQL. This includes changes to database connection settings, SQL queries, and error handling.
Solution:
Code Review: Conduct a comprehensive review of application code to identify and modify Oracle-specific SQL queries and database interactions.
Testing: Implement extensive testing to ensure that applications function correctly with the new PostgreSQL database.
7. Training and Expertise
Challenge: The migration process requires a deep understanding of both Oracle and PostgreSQL. Lack of expertise in PostgreSQL can be a significant barrier.
Solution:
Training Programs: Invest in training programs for database administrators and developers to build expertise in PostgreSQL.
Consultants: Consider hiring experienced consultants or engaging with vendors who specialize in database migrations.
8. Downtime and Business Continuity
Challenge: Minimizing downtime during the migration is crucial for maintaining business continuity. Unexpected issues during migration can lead to extended downtime and disruptions.
Solution:
Detailed Planning: create a comprehensive migration plan with detailed timelines and possibility plans for potential issues.
Incremental Migration: Consider incremental or phased migration approaches to reduce downtime and ensure a smoother transition.
Elevating Data Operations: The Impact of PostgreSQL Migration on Innovation
PostgreSQL Migration not only enhances data management capabilities but also positions organizations to better adapt to future technological advancements. With careful management of the PostgreSQL migration process, businesses can unlock the full potential of PostgreSQL, driving innovation and efficiency in their data operations. From Oracle to PostgreSQL: Effective Strategies for a Smooth Migration Navigating the migration from Oracle to PostgreSQL involves overcoming several challenges, from schema conversion to data integrity and performance optimization. Addressing these issues requires a combination of effective tools, such as Ora2Pg and AWS SCT, and strategic planning. By leveraging these tools and investing in comprehensive training, organizations can ensure a smoother transition and maintain business continuity. The key to victory lies in meticulous planning and execution, including phased migrations and thorough testing. Despite the complexities, the rewards of adopting PostgreSQL- cost efficiency, scalability, and advanced features far outweigh the initial hurdles. Thanks For Reading
For More Information, Visit Our Website: https://newtglobal.com/
0 notes
Text

#QuizTime Which database is known for its scalability and high availability?
A) Oracle 📊 B) MySQL 🛢️ C) PostgreSQL 🐘 D) All of the above ✅
Comments your answer below👇
💻 Explore insights on the latest in #technology on our Blog Page 👉 https://simplelogic-it.com/blogs/
🚀 Ready for your next career move? Check out our #careers page for exciting opportunities 👉 https://simplelogic-it.com/careers/
#quiztime#testyourknowledge#brainteasers#triviachallenge#thinkfast#quizmaster#knowledgeIspower#mindgames#database#scalability#oracle#mysql#postgresql#data#databaseservices#funfacts#simplelogicit#makingitsimple#makeitsimple#simplelogic
0 notes
Video
youtube
Amazon RDS for MariaDB | Simplify Database Management RDS for MariaDB is a fork of MySQL, offering additional features, security enhancements, and improved performance. It is fully compatible with MySQL and provides a rich ecosystem of storage engines, plugins, and tools.- Key Features: - Enhanced security features like data-at-rest encryption and data masking. - Support for MariaDB-specific features such as the Aria storage engine. - Seamless compatibility with MySQL, enabling easy migration. - Automated backups, monitoring, and maintenance.- Use Cases: - Applications needing advanced security and performance. - Users looking for an enhanced, open-source alternative to MySQL. - Web applications with moderate to high traffic.Key Benefits of Choosing the Right Amazon RDS Database:1. Optimized Performance: Select an engine that matches your performance needs, ensuring efficient data processing and application responsiveness. 2. Scalability: Choose a database that scales seamlessly with your growing data and traffic demands, avoiding performance bottlenecks. 3. Cost Efficiency: Find a solution that fits your budget while providing the necessary features and performance. 4. Enhanced Features: Leverage advanced capabilities specific to each engine to meet your application's unique requirements. 5. Simplified Management: Benefit from managed services that reduce administrative tasks and streamline database operations.Conclusion:Choosing the right Amazon RDS database engine is critical for achieving the best performance, scalability, and functionality for your application. Each engine offers unique features and advantages tailored to specific use cases, whether you need the speed of Aurora, the extensibility of PostgreSQL, the enterprise features of SQL Server, or the robustness of Oracle. Understanding these options helps ensure that your database infrastructure meets your application’s needs, both now and in the future.
#youtube#Amazon RDS RDS Monitoring AWS Performance Insights Optimize RDS Amazon CloudWatch Enhanced Monitoring AWS AWS DevOps Tutorial AWS Hands-On C#amazon auroraaurora databasecloud computingaws cloudamazon aurora deep diveamazon aurora vs rdsserverless databaseamazon aurora databaseaws#AmazonRDS RDSMonitoring PerformanceInsights CloudWatch AWSDevOps DatabaseOptimization ClouDolus ClouDolusPro
0 notes
Text
🚀 Professional Database Designer | Expert in ERD & Data Modeling 🚀
Struggling to visualize your database structure? I create clear, efficient Entity-Relationship Diagrams (ERDs) that simplify complex data and improve your system’s performance.
🔹 Tailored ERD designs for your unique business needs 🔹 Support for Oracle, MySQL, SQL Server, PostgreSQL & more 🔹 Scalable and optimized database models 🔹 Detailed documentation & expert consultation included
Let’s turn your data into a powerful asset!
👉 Hire me on PeoplePerHour now: https://www.peopleperhour.com/hourlie/professional-database-designer-erd/524486
DatabaseDesign #ERDDesign #DataModeling #DataArchitecture #DatabaseExpert #SQLDatabase #DataManagement #TechSolutions #PeoplePerHour #FreelancerLife #ITConsulting #BusinessIntelligence #DataDriven #SoftwareDevelopment #CustomDatabase #DataEngineering #DatabaseConsultant #TechFreelancer #DatabaseOptimization #DataVisualization #SystemDesign #CloudDatabase #TechSupport
0 notes
Text
What Are the Key Considerations When Planning a Fintech Product?

In the rapidly evolving world of finance, fintech software development has emerged as a key driver of innovation, convenience, and accessibility. Whether you're a startup founder or part of a traditional financial institution, developing a fintech product requires more than just technical knowledge—it demands a comprehensive understanding of finance, user behavior, regulatory frameworks, and emerging technologies. To build a successful fintech solution, there are several critical considerations you must address from the very beginning.
1. Understanding the Target Market and Problem Statement
Before writing a single line of code, it's essential to identify your target users and the financial problem you're aiming to solve. Is your product meant to simplify payments, offer better lending options, facilitate investments, or enhance insurance services? Are you targeting millennials, small businesses, rural communities, or enterprise clients?
Defining the problem statement clearly will guide the design and functionality of your product. Additionally, conducting market research helps validate the demand for your solution, assess the competition, and refine your value proposition.
2. Navigating Regulatory and Compliance Requirements
One of the most complex aspects of fintech software development is ensuring full compliance with legal and regulatory requirements. Different countries—and even different states or regions—have specific rules governing digital finance, data storage, user authentication, and financial transactions.
Common regulations include:
KYC (Know Your Customer)
AML (Anti-Money Laundering)
GDPR (for data privacy in the EU)
PCI-DSS (for payment card data security)
Planning your fintech product with compliance in mind from the outset will save time, avoid legal issues, and build trust with your users.
3. Choosing the Right Technology Stack
The technology stack you select forms the foundation of your product’s scalability, performance, and security. Some of the popular technologies used in fintech software development include:
Programming languages like Python, Java, and Kotlin
Frameworks such as React, Node.js, and Spring Boot
Cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud
Databases like PostgreSQL, MongoDB, and Oracle
The key is to choose technologies that support real-time data processing, high-level security, and easy scalability. Integration with third-party APIs, such as payment gateways, identity verification services, and banking platforms, should also be seamless and secure.
4. Prioritizing Security and Data Protection
Security is at the core of every fintech product. You’re dealing with sensitive user data—bank account numbers, identification details, transaction histories—which makes your platform a potential target for cyberattacks.
Security best practices in fintech include:
End-to-end encryption
Multi-factor authentication (MFA)
Tokenization of payment data
Regular security audits and penetration testing
Role-based access control
Additionally, implementing secure coding practices and training your development team to identify and eliminate vulnerabilities can go a long way in creating a secure fintech environment.
5. User Experience (UX) and Interface Design
No matter how powerful your backend is, a clunky and confusing user interface can drive users away. A clean, intuitive, and responsive interface is critical for adoption and engagement.
Design principles to focus on:
Ease of navigation
Minimalistic yet informative layout
Clear call-to-action buttons
Accessibility for users with disabilities
Consistent branding and visual design
The fintech landscape is extremely competitive, and often, the difference between a successful app and a forgotten one is simply superior UX.
6. Integration with Existing Financial Ecosystems
A successful fintech product often doesn't exist in isolation—it must integrate with existing banking systems, payment processors, credit bureaus, and government portals. These integrations need to be secure, real-time, and capable of handling large transaction volumes.
APIs play a major role here. Your development team should focus on building a flexible architecture that supports third-party API integrations while also allowing easy future enhancements.
7. Scalability and Performance Planning
Fintech products often experience rapid growth—especially if they solve a critical financial problem. Planning for scalability ensures that your infrastructure can handle increasing user loads, transactions, and data volumes without crashing or slowing down.
Cloud-native applications, load balancing, microservices architecture, and automated scaling are essential tools in building a robust and scalable fintech system.
8. Continuous Testing and Feedback Loops
Testing shouldn't be an afterthought. Your development process should include:
Unit testing
Integration testing
User Acceptance Testing (UAT)
Security testing
Performance testing
Once the product is launched, continuous user feedback should be used to improve features, resolve bugs, and refine UX over time. Agile methodologies and DevOps practices can support faster iteration cycles and improved product quality.
9. Cost Management and Development Timelines
Planning your budget and timeline effectively is essential for successful fintech software development. Overruns in either can stall your project or reduce its market competitiveness. Prioritize features using a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) approach and plan for incremental improvements.
10. Partnering with the Right Development Team
Lastly, success in fintech often depends on having the right tech partner. A team that understands both fintech services and the intricacies of the financial industry can bring strategic insights and avoid costly mistakes. For example, Xettle Technologies has built a reputation for delivering secure, scalable, and innovative fintech solutions by combining deep financial expertise with advanced development practices.
Conclusion
Planning a fintech product is a multifaceted process that requires thoughtful strategy, technical excellence, and a deep understanding of user needs and regulations. By considering aspects like compliance, security, scalability, and UX early in the development process, you increase your chances of building a fintech product that not only meets market demands but also leads in innovation and trust.
0 notes